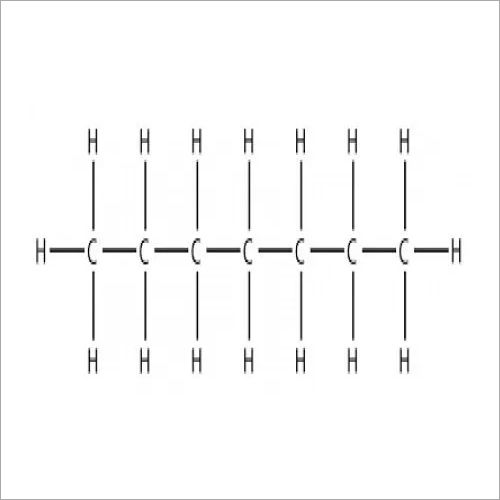
N Heptane Chemical
Product Details:
- Physical Form Liquid
- Storage Room Temperature
- Application Pharmaceutical
- Click to View more
X
N Heptane Chemical Price And Quantity
- 1 Piece
N Heptane Chemical Product Specifications
- Pharmaceutical
- Room Temperature
- Liquid
N Heptane Chemical Trade Information
- 50 Piece Per Month
- 7 Days
- All India
Product Description
Like all alkanes (paraffins, saturated hydrocarbons), n-heptane isa very good solvent for non-polar substances, fats and oils. Especially in the pharmaceutical industry, it is used as an inert solvent, for purification, recrystallization and washing of active pharmaceutical ingredients (API).
Tell us about your requirement

Price:
Quantity
Select Unit
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
Additional detail
Mobile number
Email